Inbound capacity
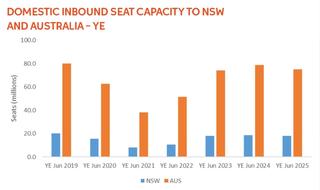
NSW domestic aviation capacity (17,964,876 seats, down 4.4 per cent compared to the 2023–24 financial year) accounted for 23.9 per cent of total domestic seats across Australia, ranking the state second nationally.
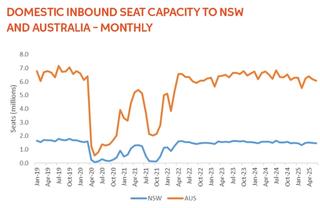
Domestic seat capacity in NSW plateaued after rebounding in mid-2022 from COVID-19 lows.
In the 2024–25 financial year, capacity declined compared to the 2023–24 financial year reaching 88.8 per cent of the 2018–19 financial year levels.
In the 2024–25 financial year, the months with domestic aviation
capacity closest to full recovery were July (91.6 per cent), June (91.3 per cent) and August (89.9 per cent).
Total inbound seats (NSW)
FY2024–25: 17,964,876
% Change vs FY2023–24: -4.4%
% Change vs FY2018–19: -11.2%
In the 2024–25 financial year, Sydney Airport received the highest number of inbound domestic seats to NSW (15,430,126 seats – 85.9 per cent of all domestic arrivals into NSW), including from intrastate destinations.
Sydney featured prominently among Australia’s busiest interstate routes, with three of the top five national routes: Melbourne to Sydney, Brisbane to Sydney and Gold Coast to Sydney.
Within NSW, the top three intrastate routes were Sydney to Ballina, Sydney to Coffs Harbour and Sydney to Dubbo.
Complementing Sydney Airport’s domestic capacity, the remaining top five NSW airports by inbound domestic seat volume were Newcastle (721,516), Ballina (357,493), Coffs Harbour (173,439) and Dubbo (170,254).
The top four airlines operating domestic services into NSW by seat were Qantas, Virgin Australia, Jetstar and Regional Express.
Inbound traffic
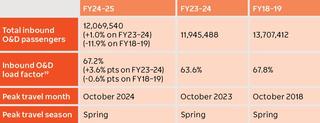
In the 2024–25 financial year, NSW saw 12,069,540 inbound domestic Origin & Destination (O&D) passengers, marking an increase from the 2023–24 financial year.
Despite the growth, volumes remain below those recorded in the 2018–19 financial year.
The leading source markets of domestic inbound O&D traffic to NSW in the 2024–25 financial year were Melbourne, Brisbane and the Gold Coast.
These top three markets remained consistent with those observed in both 2023–24 and 2018–19 financial years.